NEW Setfos Thermal Module
The new Thermal Module is the latest addition to our Setfos simulation software and has been developed to allow researchers to simulate how heat is generated, flows through the device stack, and impacts device behavior. Run thermal-only studies or fully coupled electro-thermal simulations of OLEDs, solar cells, photodetectors, and thermoelectric devices.
Key Capabilities
Stand-alone thermal or coupled electro-thermal.
Various heat sources: optical absorption, Joule heating, Thomson–Peltier heating, non-radiative recombination.
All domains: Steady-state, transient, and small-signal (AC) analyses.
Position- and time-resolved results.
OLED degradation modeling.
How to use the Thermal Module
Use the Setfos Thermal Module to quantify device temperature rise and heat flow, and assess its consequences on the electro-optical response under actual driving conditions:
Compare steady vs pulsed OLED operation.
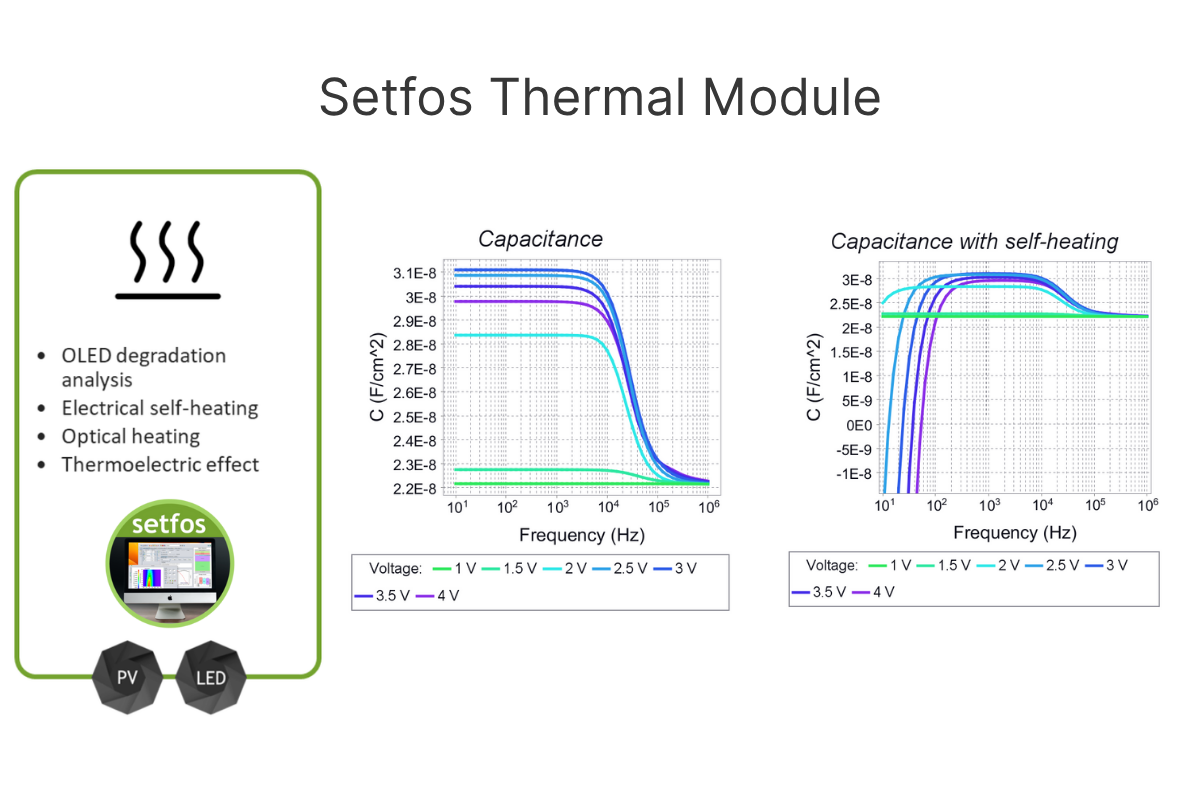
Investigate impact of self-heating on apparent device capacitance.
Identify critical operation conditions such as thermal runaway effect.
Model PV heating from optical absorption at various spectra and illumination.
Simulate electro-thermal devices (Seebeck-Peltier-effect).
Coupling Modes
The thermal model can be coupled to other Setfos modules depending on the simulation requirements,:
Optical + Thermal: Calculates the local heat generation from optical absorption.
Drift-Diffusion + Thermal: Performs a self-consistently coupled charge transport simulations, including the local temperature distribution affected by Joule heating, Thomson–Peltier effects, non-radiative recombination, with optionally from additional optical absorption.
Standalone Thermal: Used for simulating passive position- and time-resolved heat flow and storge.
Thermal Boundary Conditions
Setfos lets you define realistic thermal boundaries with configurable ambient, convective, and radiative exchange.

Try data fitting and device simulation in Setfos
Fit measurement data and test physics-based models before your next experiment.
Advanced OLED Modeling: Degradation Model
The Thermal Module license also extends the Drift-Diffusion model with advanced features to model OLED device degradation due to the formation of defects.
Simulate the local generation of defects as a function of the operation time and analyze their impact on the device performance
Couple the trap formation to various excitonic processes like TTA, TPQ
Mitigate degradation scenarios and increase OLED lifetime by optimized device design
Thermal Module FAQs
-
The Setfos Thermal Module quantifies temperature rise, heat flux, and heating contributions in layered semiconductor devices such as OLEDS and solar cells.
-
Yes, activating both Drift-Diffusion and Thermal modes automatically enables the self-consistently coupled simulation mode. The thermal model can also be coupled to the Absorption Module to consider heat generation from optical absorption.
-
Dirichlet, convective, and radiative boundaries with optional thermal capacitance.
-
Per-layer thermal conductivity and heat capacity, plus definition of boundary conditions.
-
Yes, to study temperature-induced features in small-signal response.
-
In addition to the modeling thermal effects it extends the Drift-Diffusion mode with an advanced model to simulate OLED device degradation due to the local formation of defects.
Setfos VIDEO LIBRARY
SETFOS Modules
ABSORPTION
EMISSION
DRIFT-DIFFUSION
Advanced Optics

T R I A L E V A L U A T I O N
TRY SETFOS FOR 1 MONTH
Experience the power of Setfos with a FREE 1-month trial. Dive into advanced simulations for OLEDs and solar cells, and see first-hand how our software can optimize your research and development. Take this opportunity to explore all the features and capabilities that Setfos offers, and discover how it can enhance your projects with precision and efficiency.