Research Paper: Drift-diffusion modeling of blue OLED degradation
Summary
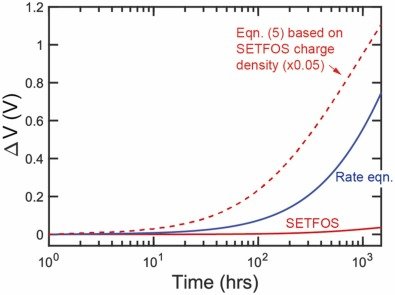
This study presents a drift-diffusion model for simulating degradation in blue OLEDs caused by exciton-polaron annihilation, and compares it to a conventional rate-equation model. The authors use Setfos to simulate luminance loss and voltage rise over time in a double heterostructure OLED architecture. Results show that although rate models can approximate overall degradation behavior, only the drift-diffusion approach accurately distinguishes between defect formation in the emissive and transport layers. The work highlights that degradation parameters fit from rate models should be treated as effective values rather than physical constants.
Publication Details
Authors: Adrian Pizano, Raju Lampande, Robert Cawthorn, Noel C. Giebink
Institution: University of Michigan, Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
Journal: Synthetic Metals
Published: 10 December 2024
Fluxim Tools Used
Simulations were performed using Setfos, Fluxim’s thin-film optics and electrical modeling software. Setfos enabled a layer-resolved analysis of degradation effects in both the emissive and transport layers, providing insight into how defect distribution impacts luminance fade and voltage rise.