Emission MODULE
Light Emission - Device Efficiency - Mode Analysis - Coatings/Filters - Parameter Fitting
Light Emission Simulation
Setfos uses the dipole emission model to predict the light emission characteristics of an OLED. Several device properties can be modelled:
Electroluminescence emission pattern.
Micro-cavity effects by thin-film optics.
Photophysical properties such as efficiency, angular color, and brightness changes.
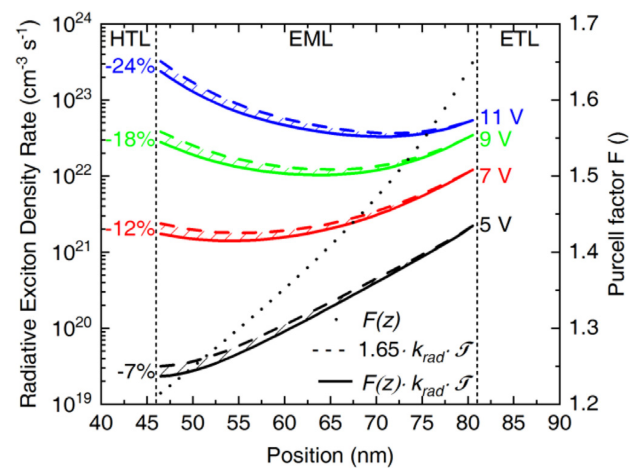
Excitonic processes in OLEDs by combining optical and electrical simulation.
Waveguided and plasmonic modes, quenching, distribution, and orientation of the emitters.
A number of scientific publications demonstrate the potential of Setfos for OLED modeling.
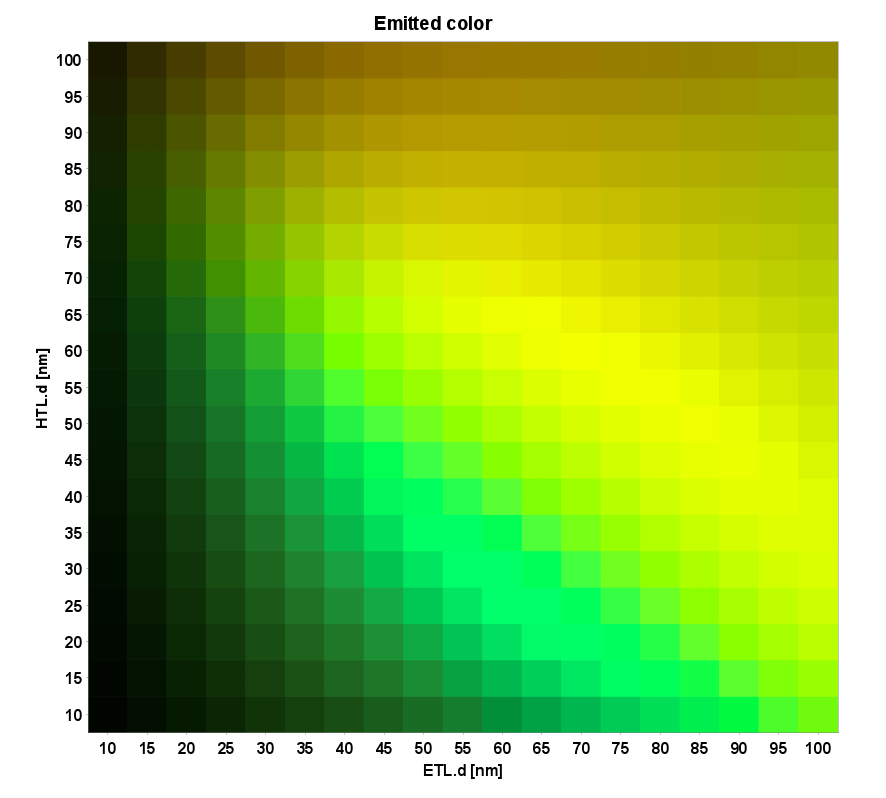
Efficiency and Emitted Color
Setfos calculates the optical parameters of an OLED by taking into account the full micro-cavity behavior. This includes but it is not limited to:
CIE xy color coordinates.
Brightness (cd/m2).
Luminous Efficacy (Lm/W).
Luminous Current Efficiency (lm/A).
Correlated Color Temperature (CCT).
Color Rendering Index (CRI).
Reflectance, transmittance, and absorbance.
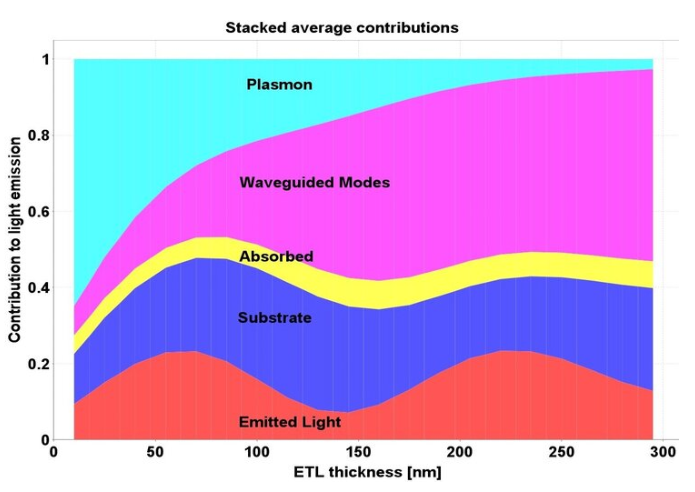
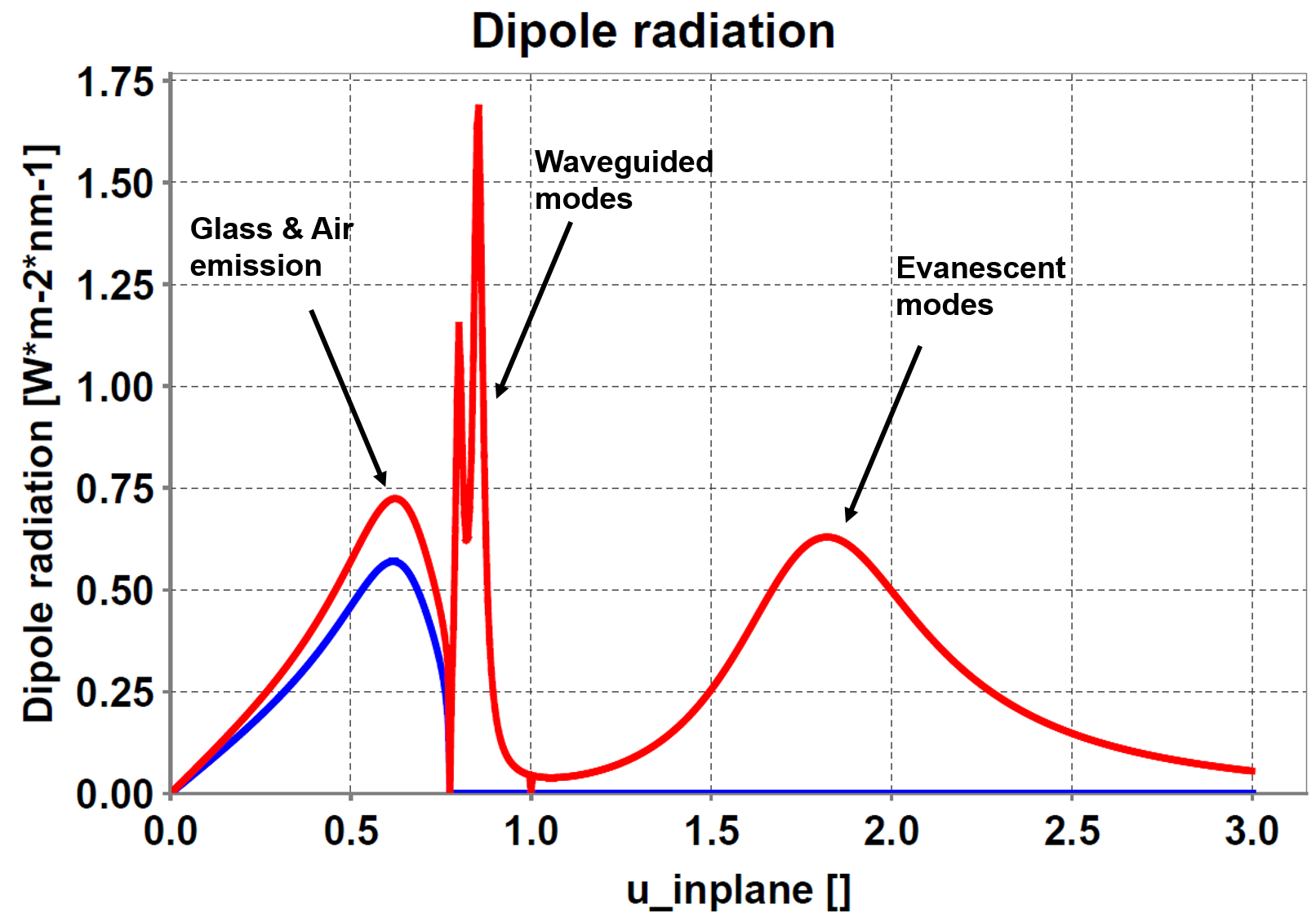
Mode Analysis
Setfos Mode Analysis can analyze light emission through the different emission channels of an OLED. The emitted light is either escaping to the far-field or waveguided inside the OLED layers. Without outcoupling structures, only the light emitted inside the escape cone is visible to the observer.
Mode analysis simulation calculates the contribution of the different optical modes to the total emitted power:
Air modes escaping to the outside.
Substrate modes waveguided in the carrier substrate.
Organic modes waveguided in the organic semiconductor stack.
Plasmon modes coupled to the metal electrodes.
Non-radiative quenching losses.
Modes can be inspected across the spectrum or summarized taking into account the spectral distribution of the emitter.
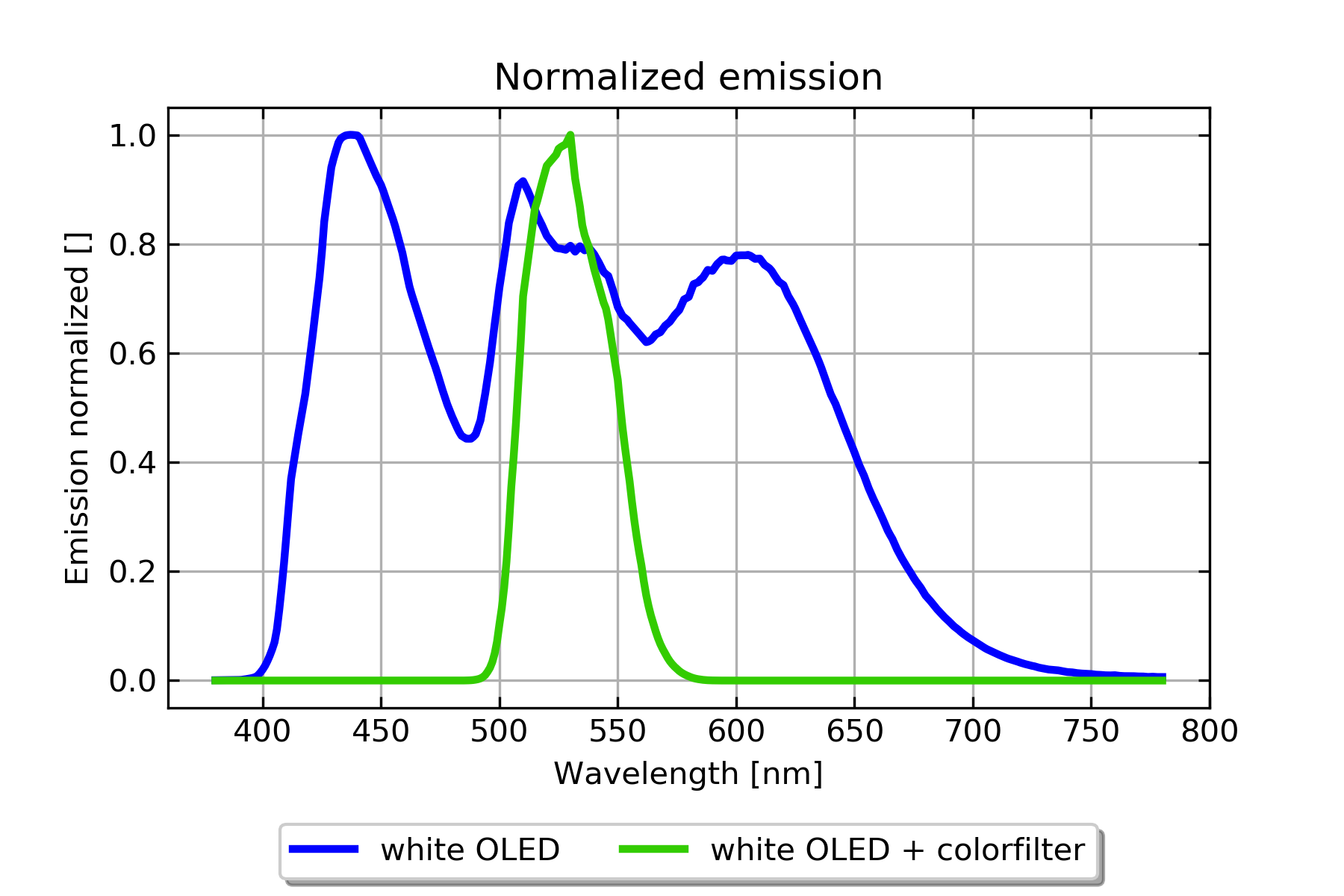
Coatings, Filters and Thin Film Optics
An OLED design is not limited to the stack of organic semiconductors. There are also color filters and anti-reflection layers that are used to obtain a higher lighting efficiency.
Setfos calculates the colour, angular variation, and polarization of the whole OLED stack, including coherent optics in the microcavity and coatings incoherently coupled through the substrate.
Emitter Profile, Optical Index, Dipole Orientation
Powerful fitting algorithms let you extract material parameters from measurement data. The optimization routines find the optimal combination of several variables.
Fitting of the emission zone in a complex multilayer stack. Find the spatial distribution of the emitting molecules.
Determine the optical n & k values from reflectance and transmittance measurement using the Sellmeier, Tauc-Lorentz, or Cauchy model.
Use spectral measurements to determine the intrinsic spectrum of an emitter/host system.
Determine the orientation of the emitter dipole by polarized spectroscopy or angular measurements.
Position-dependent Purcell Effect.